Tech Terms: Acoustic Models
Every customer conversation starts as sound – not text.
Before any AI model can detect intent, analyze sentiment, or generate summaries, it must first understand the audio itself.
That foundation comes from Acoustic Models.
They are the core technology that helps transcription engines interpret speech across accents, noise levels, languages, and environments.
How Acoustic Modeling Powers Accurate, Enterprise-Ready Transcription
In modern contact centers, Acoustic Models determine whether your downstram intelligence is accurate – or unreliable. Below, we break down what Acoustic Models are, how they work, and why they matter for enterprise-scale CX operations.
What are Acoustic Models?
Acoustic Models are machine learning models that map the raw acoustic signals of speech – pitch, tone, frequency, energy, and timing – to the sounds and patterns of human language.
Think of them as the “ears” of a transcription system. They analyze how speech sounds before any words are recognized.
Acoustic Models work alongside language models, punctuation models, and metadata systems to produce accurate, readable transcripts.
Why Acoustic Models Matter in the Enterprise
In enterprise environments, conversations rarely happen in pristine studio conditions.
Real-world audio includes:
- Background noise
- Crosstalk
- Accents and dialects
- Varying microphone quality
- Overlapping speech
- Fast – or unclear – articulation
Acoustic Models are trained to recognize and adapt to these conditions.
When Acoustic Models perform well, enterprises see:
- Higher transcription accuracy
- Better sentiment and tone detection
- More reliable search and analytics
- Stronger AI-driven insights
- Improved coaching and QA outcomes
When Acoustic Models perform poorly, everything downstream suffers.
How Acoustic Models Work, Decoded
Behind the scenes, Acoustic Models use advanced signal processing and deep learning to interpret sound.
The process typically includes:
1. Feature Extraction.
The model analyzes the waveform and extracts features like:
- Frequency patterns
- Harmonics
- Energy levels
- Timing and pauses
This creates a compact, machine-readable representation of the audio.
2. Acoustic Pattern Analysis
The model matches these features to known sound units, like phonemes and syllables.
Examples include:
- “T” vs. “D”
- “Ah” vs. “Uh”
- Rising vs. falling intonation
3. Contextual Modeling
Speech rarely exists in isolation. Acoustic Models examine patterns across time to understand how sounds flow into words.
4. Integration with Language Models
Finally, the acoustic output interacts with language models to determine the most likely word sequence.
This layered process produces the transcription you see – and the insight your tools depend on.
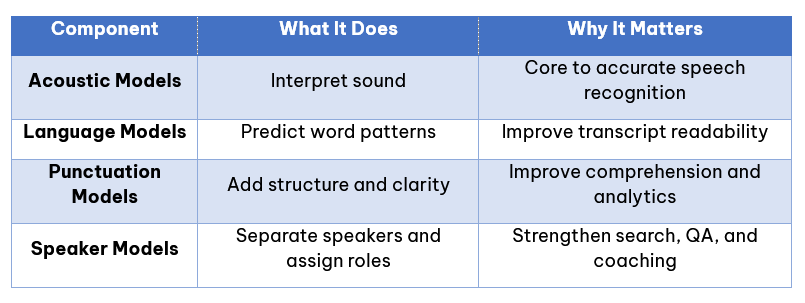
Acoustic Models vs. Other Speech Models
To increase clarity, here’s how Acoustic Models compare to related concepts:
Acoustic Models are the first step – and everything else depends on them.
Where Acoustic Models Create the Most Value
Acoustic Models are essential anywhere voice data fuels decision making:
Contact Centers. Clean transcripts improve routing, coaching, QA, and compliance.
BPOs and Outsourcing Partners. Global accents and varied audio conditions require strong acoustic adaptation.
Real-Time Applications. Low-latency acoustic processing enables live dashboards, alerts, and agent assist.
AI Insights and Analytics. Reliable acoustic recognition improves sentiment, summarization, and classification.
Machine Learning and Model Training. Better input = better training data = stronger downstram AI performance.
In every case, Acoustic Modeling ensures your voice data is trustworthy.
How NiCE ElevateAI Enhances Acoustic Modeling
At ElevateAI, Acoustic Models power both Post-Call and Real-Time Transcription across the CX and Echo transcription engines.
We deliver enterprise-level performance by designing models that:
Adapt Across Environments. Our models handle call centers, remote workspaces, mobile audio, and noisy conditions.
Support Diverse Speakers. Trained on varied accents, dialects, and vocal profiles – global and inclusive.
Maintain Low Latency. Designed for real-time use cases, with sub-second transcription.
Enhance Downstream AI. Better acoustic interpretation leads to:
- More accurate AutoSummary
- Clearer sentiment
- Stronger metadata enrichment
- Reliable Enlighten AI and CX AI scoring
Deliver Consistently Across Channels. VOice, VoIP, WebRTC, Mobile, and PSTN audio all benefit from consistent modeling.
This creates a transcription experience that is accurate, stable, and ready for enterprise scale.
Key Takeaways for Enterprise Leaders
- Definition: Acoustic Models interpret raw audio signals to understand speech patterns – forming the foundation of accurate transcriptions.
- Business Value: Strong acoustic modeling improves transcription accuracy, enhances sentiment and summarization, and strengthens analytics across the CX ecosystem.
- Enterprise Impact: Better acoustic interpretation leads to clearer transcripts, reduced QA effort, stronger outcomes, and improved customer experiences.
- The ElevateAI Advantage? ElevateAI’s acoustic modeling delivers high accuracy, multilingual performance, and real-time capability – powering every interaction with clarity and insights.
Better Audio In. Better Insights Out.
Great intelligence comes from great inputs.
Acoustic Models transform real-world audio into accurate, structured text – unlocking insight at every stage of the CX journey.
Ready to Learn More?
With NiCE ElevateAI, your voice data becomes more than a transcript.
It becomes actionable, reliable intelligence.
- Browse the ElevateAI Glossary
- Experience Real-Time Transcription
- Explore ElevateAI’s Generative AI Offerings
- Accelerate Insights with AutoSummary
- Review our Developer Documentation
- Start Building Today with ElevateAI: elevateai.com/getstarted